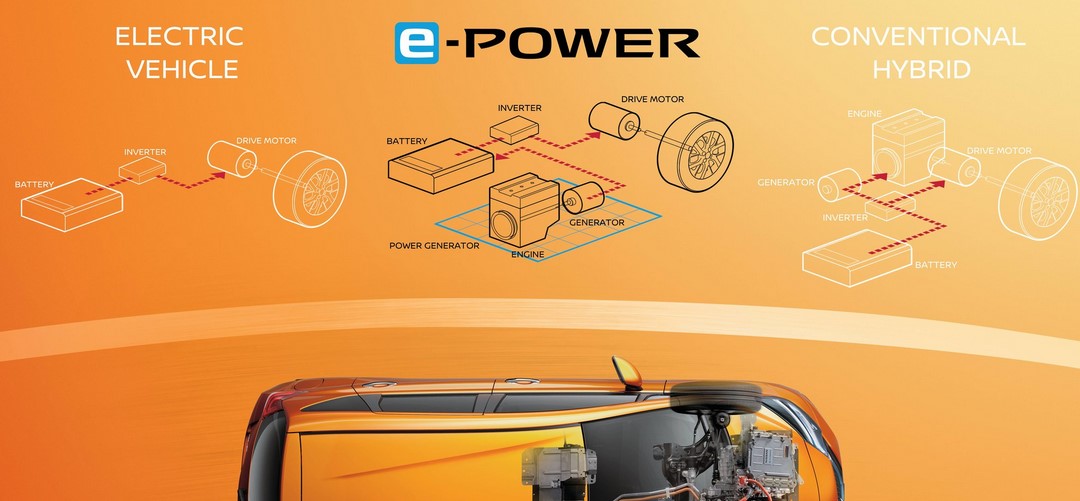
The Nissan e-Power is a hybrid electric car that was introduced in Japan in 2017 and subsequently released in other markets. It is a hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) that uses a small gasoline engine to generate electricity, which is then used to power the electric motor that drives the car. The e-Power system is unique in that it does not have a direct connection between the gasoline engine and the wheels, and the car is always powered by the electric motor. The second generation of the Nissan e-Power was released in 2020 and features a larger battery pack and improved electric drive system. It is available in several models, including the Nissan Note e-Power and the Nissan Serena e-Power.
An electric car, also known as an electric vehicle (EV), is a type of vehicle that is propelled by one or more electric motors using energy stored in rechargeable batteries. Electric cars do not have a gasoline engine and do not produce any tailpipe emissions, making them a cleaner alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. They are powered solely by electricity, which can be supplied by a variety of sources, including the electric grid, solar panels, and wind turbines. Electric cars can be charged at home or at public charging stations, and the distance they can travel on a single charge, or their range, varies depending on the make and model of the vehicle and the size of the battery. There are many benefits to driving an electric car, including lower fuel costs, reduced reliance on fossil fuels, and lower emissions. However, electric cars can be more expensive to purchase upfront, and the availability of charging infrastructure can vary depending on the location.
A hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) is a type of vehicle that combines a traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) with one or more electric motors. The electric motor is powered by a battery pack, and the vehicle can be powered by either the electric motor or the ICE, depending on the driving conditions and the state of the battery. Hybrid electric vehicles are designed to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions by using the electric motor to assist the ICE, especially during acceleration and at lower speeds. When the vehicle is decelerating or stopped, the electric motor can function as a generator to recharge the battery pack. There are several types of hybrid electric vehicles, including parallel hybrids, series hybrids, and plug-in hybrids. Hybrid electric vehicles can offer some of the benefits of both traditional gasoline-powered vehicles and electric vehicles, but they can also be more expensive to purchase upfront.